

SEMinRExtras adds functionality to the SEMinRpackage.
SEMinR (Ray, Danks, & calero-Valdez, 2026) is a domain specific language for modeling and estimating structural equation models. This is a supplementary package for SEMinR and not a standalone package. This package serves to provide additional extra methods and functions that can be used to analyze PLS-SEM models.
SEMinRExtras provides advanced SEM tools which are compatible with SEMinR. In the current version, we provide an implementation of the Cross-Validated Predictive Ability Test (CVPAT) as proposed by Liengaard et al. (2021) and Sharma et al. (2022).
SEMinRExtras also serves to host the example models used in the PLS-SEM in R workbook (Hair et al., 2026).
In order to access the demo files for the textbook, you can run the
demo() function after loading the SEMinRExtras package.
E.g.
demo("seminr-help-debugging", package = "seminrExtras")
We are applying the CVPAT process to the corporate reputation example bundled with SEMinR. Since we will be comparing two models, we will first estimate and plot both models. Below you will find the competing and established models which will be compared.
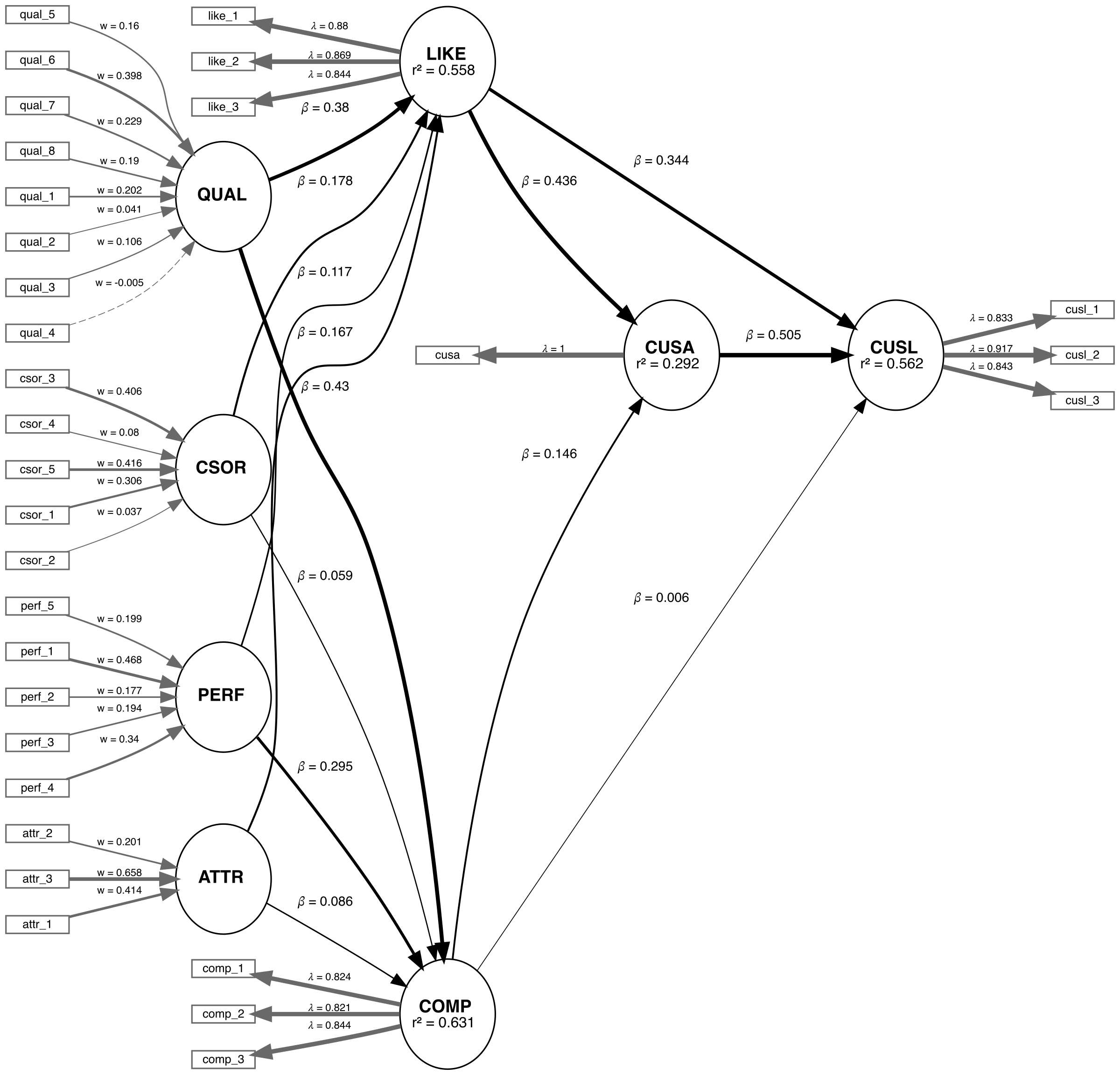
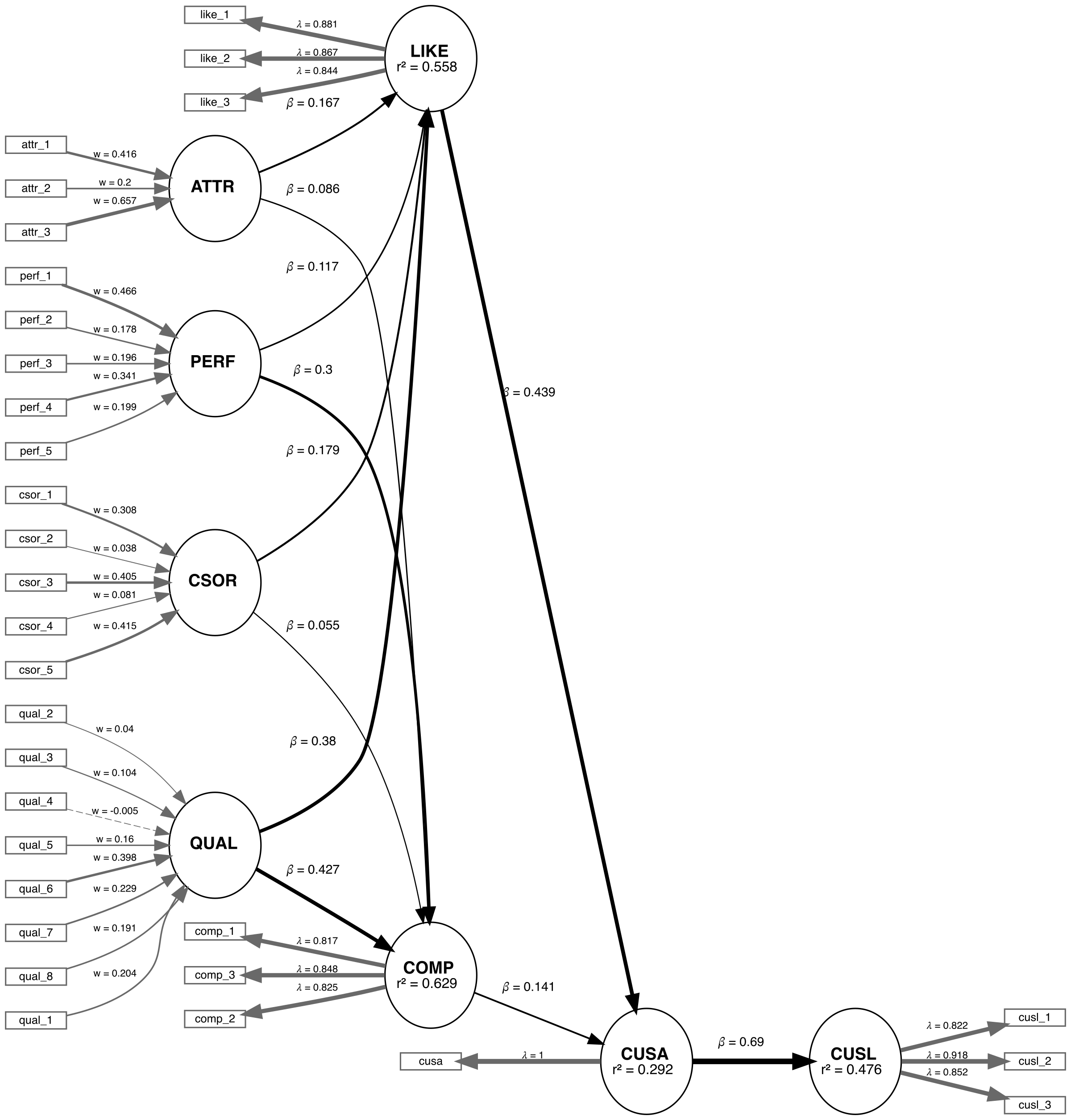
# Create measurement model ----
corp_rep_mm_ext <- constructs(
composite("QUAL", multi_items("qual_", 1:8), weights = mode_B),
composite("PERF", multi_items("perf_", 1:5), weights = mode_B),
composite("CSOR", multi_items("csor_", 1:5), weights = mode_B),
composite("ATTR", multi_items("attr_", 1:3), weights = mode_B),
composite("COMP", multi_items("comp_", 1:3)),
composite("LIKE", multi_items("like_", 1:3)),
composite("CUSA", single_item("cusa")),
composite("CUSL", multi_items("cusl_", 1:3))
)
alt_mm <- constructs(
composite("QUAL", multi_items("qual_", 1:8), weights = mode_B),
composite("PERF", multi_items("perf_", 1:5), weights = mode_B),
composite("CSOR", multi_items("csor_", 1:5), weights = mode_B),
composite("ATTR", multi_items("attr_", 1:3), weights = mode_B),
composite("COMP", multi_items("comp_", 1:3)),
composite("LIKE", multi_items("like_", 1:3)),
composite("CUSA", single_item("cusa")),
composite("CUSL", multi_items("cusl_", 1:3))
)
# Create structural model ----
corp_rep_sm_ext <- relationships(
paths(from = c("QUAL", "PERF", "CSOR", "ATTR"), to = c("COMP", "LIKE")),
paths(from = c("COMP", "LIKE"), to = c("CUSA", "CUSL")),
paths(from = c("CUSA"), to = c("CUSL"))
)
alt_sm <- relationships(
paths(from = c("QUAL", "PERF", "CSOR", "ATTR"), to = c("COMP", "LIKE")),
paths(from = c("COMP", "LIKE"), to = c("CUSA")),
paths(from = c("CUSA"), to = c("CUSL"))
)
# Estimate the models ----
established_model <- estimate_pls(
data = corp_rep_data,
measurement_model = corp_rep_mm_ext,
structural_model = corp_rep_sm_ext,
missing = mean_replacement,
missing_value = "-99")
competing_model <- estimate_pls(
data = corp_rep_data,
measurement_model = alt_mm,
structural_model = alt_sm,
missing = mean_replacement,
missing_value = "-99")
# Function to compare the Loss of two models
compare_results <- assess_cvpat_compare(established_model = established_model,
alternative_model = competing_model,
testtype = "two.sided",
nboot = 2000,
technique = predict_DA,
seed = 123,
noFolds = 10,
reps = 10,
cores = 1)
print(compare_results,
digits = 3)
# Assess the base model ----
assess_results <- assess_cvpat(established_model,
seed = 123,
cores = 1)
print(assess_results$CVPAT_compare_LM,
digits = 3)
print(assess_results$CVPAT_compare_IA,
digits = 3)# Assess the base model ----
assess_results <- assess_cvpat(established_model,
seed = 123,
cores = 1)
print(assess_results$CVPAT_compare_LM,
digits = 3)
#> PLS Loss LM Loss Diff Boot T value Boot P Value
#> COMP 1.196 1.211 -0.015 0.542 0.588
#> LIKE 1.915 2.063 -0.148 3.761 0.000
#> CUSA 0.994 0.983 0.011 -0.489 0.625
#> CUSL 1.560 1.600 -0.040 2.914 0.004
#> Overall 1.416 1.464 -0.048 3.482 0.001
#>
#> CVPAT as per Sharma et al. (2023).
print(assess_results$CVPAT_compare_IA,
digits = 3)
#> PLS Loss IA Loss Diff Boot T value Boot P Value
#> COMP 1.196 2.023 -0.827 8.580 0.000
#> LIKE 1.915 3.103 -1.187 8.293 0.000
#> CUSA 0.994 1.374 -0.379 5.004 0.000
#> CUSL 1.560 2.663 -1.102 7.572 0.000
#> Overall 1.416 2.290 -0.874 10.301 0.000
#>
#> CVPAT as per Sharma et al. (2023).The established model has significantly lower predictive loss compared to both the naive benchmark IA and the LM model. Thus, we can say that the established model has predictive relevance.
Now we compare the results:
# Function to compare the Loss of two models
compare_results <- assess_cvpat_compare(established_model = established_model,
alternative_model = competing_model,
testtype = "two.sided",
nboot = 2000,
technique = predict_DA,
seed = 123,
noFolds = 10,
reps = 10,
cores = 1)
print(compare_results,
cores = 1,
digits = 3)
#> Base Model Loss Alt Model Loss Diff Boot T value Boot P Value
#> COMP 1.198 1.195 0.003 -0.460 0.645
#> LIKE 1.923 1.933 -0.010 0.883 0.378
#> CUSA 0.988 0.992 -0.004 0.809 0.419
#> CUSL 1.562 1.715 -0.152 3.286 0.001
#> Overall 1.418 1.459 -0.041 3.293 0.001
#>
#> CVPAT as per Sharma, Liengaard, Hair, Sarstedt, & Ringle, (2023).
#> Both models under comparison have identical endoogenous constructs with identical measurement models.
#> Purely exogenous constructs can differ in regards to their relationships with both nomological
#> partners and measurement indicators.The established model has significantly lower predictive loss compared to the competing model. Thus, we can say that the established model has superior predictive performance compared to the competing model.