| Type: | Package |
| Title: | Bayes Classifier for Verbal Autopsy Data |
| Version: | 1.2 |
| Date: | 2022-04-25 |
| Maintainer: | Richard Wen <rrwen.dev@gmail.com> |
| Description: | An implementation of the Naive Bayes Classifier (NBC) algorithm used for Verbal Autopsy (VA) built on code from Miasnikof et al (2015) <doi:10.1186/s12916-015-0521-2>. |
| Depends: | R (≥ 4.0.0) |
| Imports: | graphics, methods, utils, shiny |
| Suggests: | bookdown, knitr, rmarkdown, testthat |
| Enhances: | openVA |
| License: | GPL-3 |
| LazyData: | TRUE |
| RoxygenNote: | 7.1.2 |
| Collate: | 'nbc4va.R' 'nbc4va_data.R' 'nbc4va_validation.R' 'nbc4va_internal.R' 'nbc4va_main.R' 'nbc4va_extra.R' 'nbc4va_utility.R' 'nbc4va_wrapper.R' |
| VignetteBuilder: | knitr |
| Encoding: | UTF-8 |
| NeedsCompilation: | no |
| Packaged: | 2022-05-09 12:05:12 UTC; rrwen |
| Author: | Richard Wen [aut, cre], Pierre Miasnikof [ctb], Vasily Giannakeas [ctb], Mireille Gomes [ctb] |
| Repository: | CRAN |
| Date/Publication: | 2022-05-10 10:40:02 UTC |
Calculate predicted CSMFs from a NBC model
Description
Obtains the predicted Cause Specific Mortality Fraction (CSMF) from a result nbc object.
Usage
csmf.nbc(object)
Arguments
object |
The result |
Value
out A numeric vector of the predicted CSMFs in which the names are the corresponding causes.
See Also
Other wrapper functions:
topCOD.nbc()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaData)
# Run naive bayes classifier on random train and test data
train <- nbc4vaData[1:50, ]
test <- nbc4vaData[51:100, ]
results <- nbc(train, test)
# Obtain the predicted CSMFs
predCSMF <- csmf.nbc(results)
Check arguments for nbc()
Description
Performs checks to ensure that the arguments passed to internalNBC are correct.
This function will also auto-clean when appropriate, and display
warning messages of the cleaning tasks.
Usage
internalCheckNBC(train, test, known = TRUE, assume = FALSE, unknown = 99)
Arguments
train |
Dataframe of verbal autopsy train data (See Data documentation).
Example:
| ||||||||||||||||||||
test |
Dataframe of verbal autopsy test data in the same format as train except if causes are not known:
| ||||||||||||||||||||
known |
TRUE to indicate that the test causes are available in the 2nd column and FALSE to indicate that they are not known | ||||||||||||||||||||
assume |
TRUE to set all symptoms not equal to 1 as 0 and FALSE to raise error if symptoms are not 0 or 1. This takes priority over unknown. | ||||||||||||||||||||
unknown |
A single integer value which determines if a symptom is unknown as to if is present or absent.
|
Details
The following checks are applied to train and test to ensure they:
are a dataframe
have required number of rows and columns
have required data types for each column
have required symptom values
are in the same format
have unique ids
Value
out A list object containing the checked inputs:
$train: dataframe of id, cause and symptoms
$test: dataframe of id, cause and symptoms in the same format as train
$known: TRUE if the test causes are known or FALSE if not
See Also
Other validation functions:
internalCheckNBCSummary()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaData)
# Check train and test inputs, error if it does not pass check
train <- nbc4vaData[1:50, ]
test <- nbc4vaData[51:100, ]
checked <- nbc4va::internalCheckNBC(train, test)
train <- checked$train
test <- checked$test
Check arguments for summary.nbc()
Description
Performs checks to ensure that the arguments passed to summary.nbc are correct.
This function will perform automatic data type conversions, and display warnings when appropriate.
Usage
internalCheckNBCSummary(object, top = 5, id = NULL, csmfa.obs = NULL, ...)
Arguments
object |
The result |
top |
A number that produces top causes depending on id:
|
id |
A character representing a case id in the test data. |
csmfa.obs |
A character vector of the true causes for calculating the CSMF accuracy. |
... |
Additional arguments to be passed if applicable |
Details
The following checks are applied:
-
object is of class "nbc"
-
top is a numeric value of length 1
-
id is NULL or a character of length 1, and exists in the test data
-
csmfa.obs is NULL or a character or vector of characters
Value
out A list object containing the checked inputs:
$object: an
nbcobject$top: numeric value
$id: NULL or character value
$csmfa.obs: NULL or character vector
See Also
Other validation functions:
internalCheckNBC()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaData)
# Create an nbc
train <- nbc4vaData[1:50, ]
test <- nbc4vaData[51:100, ]
results <- nbc(train, test)
# Check the inputs before passing on to summary
checked <- nbc4va::internalCheckNBCSummary(results, 5, "g85")
results <- checked$object
top <- checked$top
id <- checked$id
csmfa.obs <- checked$csmfa.obs
Calculate CSMF accuracy
Description
Calculates the overall CSMF accuracy given any number of predicted cases and any number of observed cases.
Usage
internalGetCSMFAcc(pred, obs)
Arguments
pred |
Chracter vector of predicted causes for each case. |
obs |
Character vector of observed causes for each case. |
Value
csmfa Numeric value of the overall CSMF accuracy (see Methods documentation).
See Also
Other internal functions:
internalGetCSMFMaxError(),
internalGetCauseMetrics(),
internalGetMetrics(),
internalNBC()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
pred <- c("HIV", "Stroke", "HIV", "Stroke")
obs <- c("HIV", "HIV", "Stroke", "Stroke")
csmfa <- nbc4va::internalGetCSMFAcc(pred, obs)
Calculate CSMF maximum error
Description
Calculates the CSMF maximum error given a set of observed cases.
Usage
internalGetCSMFMaxError(obs)
Arguments
obs |
Character vector of observed causes for each case. |
Value
csmfMaxError Numeric value of the CSMF maximum error (see Methods documentation).
See Also
Other internal functions:
internalGetCSMFAcc(),
internalGetCauseMetrics(),
internalGetMetrics(),
internalNBC()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
obs <- c("HIV", "HIV", "Stroke", "Stroke")
maxerror <- nbc4va::internalGetCSMFMaxError(obs)
Calculate performance metrics table per cause
Description
A table providing performance metrics per unique cause based on input predicted and observed cases.
Usage
internalGetCauseMetrics(pred, obs, causes = unique(c(pred, obs)))
Arguments
pred |
Chracter vector of predicted causes for each case. |
obs |
Character vector of observed causes for each case. |
causes |
Character vector of all possible causes including ones that are not in the pred or obs. |
Details
This code is built on the original performance metrics code provided by Dr. Mireille Gomes.
Value
out Dataframe of a performance metrics per cause (see Methods documentation):
Columns: Cause, TruePositives, TrueNegatives, FalsePositives, FalseNegatives, PredictedFrequency, ObservedFrequency, Sensitivity, CSMFpredicted, CSMFobserved
Cause (vectorof char): The unique causes from both the obs and pred inputs
Sensitivity (vectorof double): the sensitivity for a cause
CSMFpredicted (vectorof double): the cause specific mortality fraction for a cause given the predicted deaths
CSMFobserved (vectorof double): the cause specific mortality fraction for a cause given the observed deaths
TruePositives (vectorof double): The total number of true positives per cause
TrueNegatives (vectorof double): The total number of true negatives per cause
FalsePositives (vectorof double): The total number of false positives per cause
FalseNegatives (vectorof double): The total number of false negatives per cause
PredictedFrequency (vectorof double): The occurence of a cause in the pred input
ObservedFrequency (vectorof double): The occurence of a cause in the obs input
Example:
| Cause | Sensitivity | Metric-n.. |
| HIV | 0.5 | #.. |
| Stroke | 0.5 | #.. |
See Also
Other internal functions:
internalGetCSMFAcc(),
internalGetCSMFMaxError(),
internalGetMetrics(),
internalNBC()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
pred <- c("HIV", "Stroke", "HIV", "Stroke")
obs <- c("HIV", "HIV", "Stroke", "Stroke")
cmetrics <- nbc4va::internalGetCauseMetrics(pred, obs)
Calculate overall performance metrics
Description
A vector providing overall performance metrics based on input predicted and observed cases.
Usage
internalGetMetrics(
pred,
obs,
causes = unique(c(pred, obs)),
csmfa.obs = NULL,
causeMetrics = internalGetCauseMetrics(pred, obs, causes)
)
Arguments
pred |
Chracter vector of predicted causes for each case. |
obs |
Character vector of observed causes for each case. |
causes |
Character vector of all possible causes including ones that are not in the pred or obs. |
csmfa.obs |
A character vector of the true causes for calculating the CSMF accuracy. |
causeMetrics |
Dataframe of a performance metrics per cause (see
|
Details
Developer Note: Depends on the internalGetCSMFAcc function to get the CSMF Accuracy.
Value
metrics Named numeric vector of performance metrics (see Methods documentation):
Names: TruePositives, TrueNegatives, FalsePositives, FalseNegatives, Accuracy, Sensitivity, Specificity, PCCC, CSMFMaxError, CSMFaccuracy
TruePositives (double): total number of true positives
TrueNegatives (double): total number of true negatives
FalsePositives (double): total number of false positives
FalseNegatives (double): total number of false negatives
Sensitivity (double): the overall sensitivity
PCCC (double): the partial chance corrected concordance
CSMFMaxError (double): the maximum Cause Specific Mortality Fraction Error
CSMFaccuracy (double): the Cause Specific Mortaliy Fraction accuracy
See Also
Other internal functions:
internalGetCSMFAcc(),
internalGetCSMFMaxError(),
internalGetCauseMetrics(),
internalNBC()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
pred <- c("HIV", "Stroke", "HIV", "Stroke")
obs <- c("HIV", "HIV", "Stroke", "Stroke")
metrics <- nbc4va::internalGetMetrics(pred, obs)
NBC algorithm source code
Description
Performs Naive Bayes Classification given train and test (validation) datasets, as well as additional information for the train and test data.
Usage
internalNBC(train, test, known = TRUE)
Arguments
train |
Dataframe of verbal autopsy train data (See Data documentation).
Example:
| ||||||||||||||||||||
test |
Dataframe of verbal autopsy test data in the same format as train except if causes are not known:
| ||||||||||||||||||||
known |
TRUE to indicate that the test causes are available in the 2nd column and FALSE to indicate that they are not known |
Details
This function was built on code provided by Miasnikof et al (2015). Edits to the code included the following improvements:
Causes can be character type
Matrix operations for speed
Removal of order dependence for causes
Refactoring of variable names for clarity
Included list structure of model data and details
Argument validation
Value
out The result list object containing:
$prob.causes (vectorof double): the probabilities for each test case prediction by case id
$pred.causes (vectorof char): the predictions for each test case by case id
Additional values:
* indicates that the value is only available if test causes are known
$train (dataframe): the input train data
$train.ids (vectorof char): the ids of the train data
$train.causes (vectorof char): the causes of the train data by case id
$train.samples (double): the number of input train samples
$test (dataframe): the input test data
$test.ids (vectorof char): the ids of the test data
$test.causes* (vectorof char): the causes of the test data by case id
$test.samples (double): the number of input test samples
$test.known (logical): whether the test causes are known
$symptoms (vectorof char): all unique symptoms in order
$causes (vectorof char): all possible unique causes of death
$causes.train (vectorof char): all unique causes of death in the train data
$causes.test* (vectorof char): all unique causes of death in the test data
$causes.pred (vectorof char): all unique causes of death in the predicted cases
$causes.obs* (vectorof char): all unique causes of death in the observed cases
$pred (dataframe): a table of predictions for each test case, sorted by probability
Columns (in order): CaseID, TrueCause, Prediction-1 to Prediction-n..
CaseID (vectorof char): case identifiers
TrueCause* (vectorof char): the observed causes of death
Prediction-n.. (vectorsof char): the predicted causes of death, where Prediction1 is the most probable cause, and Prediction-n is the least probable cause
Example:
CaseID Prediction1 Prediction2 "a1" "HIV" "Stroke" "b2" "Stroke" "HIV" "c3" "HIV" "Stroke" $obs* (dataframe): a table of observed causes matching $pred for each test case
Columns (in order): CaseID, TrueCause
CaseID (vectorof char): case identifiers
TrueCause (vectorof char): the actual cause of death if applicable
Example:
CaseID TrueCause "a1" "HIV" "b2" "Stroke" "c3" "HIV" $obs.causes* (vectorof char): all observed causes of death by case id
$prob (dataframe): a table of probabilities of each cause for each test case
Columns (in order): CaseID, Cause-1 to Cause-n..
CaseID (vectorof char): case identifiers
Cause-n.. (vectorsof double): probabilies for each cause of death
Example:
CaseID HIV Stroke "a1" 0.5 0.5 "b2" 0.3 0.7 "c3" 0.9 0.1
Author(s)
Pierre Miasnikof (Original), Vasily Giannakeas (Original), Richard Wen (Edits) <wenr@smh.ca>
References
Miasnikof P, Giannakeas V, Gomes M, Aleksandrowicz L, Shestopaloff AY, Alam D, Tollman S, Samarikhalaj, Jha P. Naive Bayes classifiers for verbal autopsies: comparison to physician-based classification for 21,000 child and adult deaths. BMC Medicine. 2015;13:286. doi:10.1186/s12916-015-0521-2.
See Also
Other internal functions:
internalGetCSMFAcc(),
internalGetCSMFMaxError(),
internalGetCauseMetrics(),
internalGetMetrics()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaData)
# Create naive bayes classifier on random train and test data
# Set "known" to indicate whether or not "test" causes are known
train <- nbc4vaData[1:50, ]
test <- nbc4vaData[51:100, ]
results <- nbc4va::internalNBC(train, test, known=TRUE)
# Obtain the probabilities and predictions
prob <- results$prob.causes
pred <- results$pred.causes
Round values to whole numbers while preserving the sum
Description
Rounds a vector of values to whole numbers while preserving the sum (rounded if it is not a whole number) using the largest remainder method (Gallagher, 1991).
Usage
internalRoundFixedSum(v, roundSum = round)
Arguments
v |
A vector of values with decimal values and a whole number sum to round. |
roundSum |
If the sum of the values in v is not a whole number, choose a rounding method to ensure it is a whole number. |
Value
out A vector of v with the values rounded to whole numbers but with the whole number sum preserved.
References
Gallagher M. Proportionality, disproportionality and electoral systems. Electoral Studies. 1991;10(1)33-51. doi:10.1016/0261-3794(91)90004-C.
See Also
Other data functions:
internalSubAsRest()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
dec <- c(rep(50/2, 2), rep(50/3, 3))
whole <- nbc4va::internalRoundFixedSum(dec)
Substitute values in a dataframe proportionally to all other values
Description
Substitute a target value proportionally to the distribution of the rest of the values in a column, given the following conditions:
If a column contains only the target value, the column is removed
If there are not enough target values to be distributed, then each target value will be randomly sampled from the rest of the column values with replacement
Usage
internalSubAsRest(
dataset,
x,
cols = 1:ncol(dataset),
ignore = c(NA, NaN),
removal = FALSE
)
Arguments
dataset |
A dataframe with value(s) of x in it. |
x |
A target value in dataframe to replace with the rest of values per column. |
cols |
A numeric vector of columns to consider for substitution. |
ignore |
A vector of the rest of the values to ignore for substitution. |
removal |
Set to TRUE to remove column(s) that consist only of x values. |
Details
Pseudocode of algorithm:
SET dataset = table of values with columns and rows
SET x = target value for substitution
IF x in dataset:
FOR EACH column y in a dataset:
SET xv = all x values in y
SET rest = all values not equal to x in y
IF xv == values in y:
REMOVE y in dataset
IF number of unique values of rest == 1:
MODIFY xv = rest
IF number of xv values < number of unique values of rest:
SET xn = number of xv values
MODIFY xv = random sample of rest with size xn
ELSE:
SET xn = number of xv values
SET p = proportions of rest
SET xnp = xn * p
IF xnp has decimals:
MODIFY xnp = round xnp such that sum(xnp) == xn via largest remainder method
MODIFY xv = rest values with distribution of xnp
RETURN dataset
Value
out A dataframe or list depending on removal:
if (removal is FALSE) return the dataset with values of x substituted by the rest of the values per column
if (removal is TRUE) return a list with the following:
$removed (vectorof numeric): the removed column indices if the column(s) consists only of x values
$dataset (dataframe): the dataset with values of x substituted by the rest of the values per column
See Also
Other data functions:
internalRoundFixedSum()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaDataRaw)
unclean <- nbc4vaDataRaw
clean <- nbc4va::internalSubAsRest(unclean, 99)
Train a NBC model
Description
Performs supervised Naive Bayes Classification on verbal autopsy data.
Usage
nbc(train, test, known = TRUE)
Arguments
train |
Dataframe of verbal autopsy train data (See Data documentation).
Example:
| ||||||||||||||||||||
test |
Dataframe of verbal autopsy test data in the same format as train except if causes are not known:
| ||||||||||||||||||||
known |
TRUE to indicate that the test causes are available in the 2nd column and FALSE to indicate that they are not known |
Value
out The result nbc list object containing:
$prob.causes (vectorof double): the probabilities for each test case prediction by case id
$pred.causes (vectorof char): the predictions for each test case by case id
Additional values:
* indicates that the value is only available if test causes are known
$train (dataframe): the input train data
$train.ids (vectorof char): the ids of the train data
$train.causes (vectorof char): the causes of the train data by case id
$train.samples (double): the number of input train samples
$test (dataframe): the input test data
$test.ids (vectorof char): the ids of the test data
$test.causes* (vectorof char): the causes of the test data by case id
$test.samples (double): the number of input test samples
$test.known (logical): whether the test causes are known
$symptoms (vectorof char): all unique symptoms in order
$causes (vectorof char): all possible unique causes of death
$causes.train (vectorof char): all unique causes of death in the train data
$causes.test* (vectorof char): all unique causes of death in the test data
$causes.pred (vectorof char): all unique causes of death in the predicted cases
$causes.obs* (vectorof char): all unique causes of death in the observed cases
$pred (dataframe): a table of predictions for each test case, sorted by probability
Columns (in order): CaseID, TrueCause, Prediction-1 to Prediction-n..
CaseID (vectorof char): case identifiers
TrueCause* (vectorof char): the observed causes of death
Prediction-n.. (vectorsof char): the predicted causes of death, where Prediction1 is the most probable cause, and Prediction-n is the least probable cause
Example:
CaseID Prediction1 Prediction2 "a1" "HIV" "Stroke" "b2" "Stroke" "HIV" "c3" "HIV" "Stroke" $obs* (dataframe): a table of observed causes matching $pred for each test case
Columns (in order): CaseID, TrueCause
CaseID (vectorof char): case identifiers
TrueCause (vectorof char): the actual cause of death if applicable
Example:
CaseID TrueCause "a1" "HIV" "b2" "Stroke" "c3" "HIV" $obs.causes* (vectorof char): all observed causes of death by case id
$prob (dataframe): a table of probabilities of each cause for each test case
Columns (in order): CaseID, Cause-1 to Cause-n..
CaseID (vectorof char): case identifiers
Cause-n.. (vectorsof double): probabilies for each cause of death
Example:
CaseID HIV Stroke "a1" 0.5 0.5 "b2" 0.3 0.7 "c3" 0.9 0.1
References
Miasnikof P, Giannakeas V, Gomes M, Aleksandrowicz L, Shestopaloff AY, Alam D, Tollman S, Samarikhalaj, Jha P. Naive Bayes classifiers for verbal autopsies: comparison to physician-based classification for 21,000 child and adult deaths. BMC Medicine. 2015;13:286. doi:10.1186/s12916-015-0521-2.
See Also
Other main functions:
plot.nbc(),
print.nbc_summary(),
summary.nbc()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaData)
# Run naive bayes classifier on random train and test data
# Set "known" to indicate whether or not "test" causes are known
train <- nbc4vaData[1:50, ]
test <- nbc4vaData[51:100, ]
results <- nbc(train, test, known=TRUE)
# Obtain the probabilities and predictions
prob <- results$prob.causes
pred <- results$pred.causes
nbc4va: Bayes Classifier for Verbal Autopsy Data
Description
An implementation of the Naive Bayes Classifier (NBC) algorithm
used for Verbal Autopsy (VA) built on code from Miasnikof et al (2015) <DOI:10.1186/s12916-015-0521-2>.
For documentation and help, please see:
https://rrwen.github.io/nbc4va/
Acknowledgements
This package was developed at the Centre for Global Health Research (CGHR) in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The original NBC algorithm code was developed by Pierre Miaskinof and Vasily Giannakeas. The original performance metrics code was provided by Dr. Mireille Gomes whom also offered guidance in metrics implementation and user testing. Special thanks to Richard Zehang Li for providing a standard structure for the package and Patrycja Kolpak for user testing of the GUI.
Author(s)
Richard Wen <rrwen.dev@gmail.com>
References
Use citation("nbc4va") to view citation information for the nbc4va package.
Miasnikof P, Giannakeas V, Gomes M, Aleksandrowicz L, Shestopaloff AY, Alam D, Tollman S, Samarikhalaj, Jha P. Naive Bayes classifiers for verbal autopsies: comparison to physician-based classification for 21,000 child and adult deaths. BMC Medicine. 2015;13:286. doi:10.1186/s12916-015-0521-2.
Examples
## Not run:
library(nbc4va)
# Quick start
# Follow the instructions in the web interface
nbc4vaGUI()
# View user guides for the nbc4va package
browseVignettes("nbc4va")
## End(Not run)
Example of clean data in nbc4va
Description
A random generation of clean verbal autopsy synthetic data for use in demonstrating the nbc4va package.
Usage
nbc4vaData
Format
A dataframe with 100 rows and 102 columns:
id (vectorof char): the case identifiers
cause (vectorof char): the cause of death for each case
symptom1..100 (vectorsof (1 OR 0)): whether the symptom is recorded as present (1) or not (0) for each case (row)
Example:
id cause symptom1 symptom2 symptom3 "a27" "cause10" 1 0 0 "k37" "cause2" 0 0 1 "e57" "cause8" 1 0 0
Source
Random generation using the sample function with set.seed set to 1.
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaData)
Example of unclean data in nbc4va
Description
A random generation of unclean verbal autopsy synthetic data for use in demonstrating the nbc4va package.
Usage
nbc4vaDataRaw
Format
A dataframe with 100 rows and 102 columns:
id (vectorof char): the case identifiers
cause (vectorof char): the cause of death for each case
symptom1..100 (vectorsof (1 OR 0 OR 99)): whether the symptom is recorded as present (1), absent (0), or unknown (99) for each case (row)
Example:
id cause symptom1 symptom2 symptom3 "a27" "cause10" 99 0 1 "k37" "cause2" 0 99 1 "e57" "cause8" 1 0 99
Details
Warning: This data may produce errors depending on how you use it in the package.
Source
Random generation using the sample function with set.seed set to 1.
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaDataRaw)
Web-based graphical user interface in nbc4va
Description
A Graphical User Interface (GUI) for the nbc4va package using shiny.
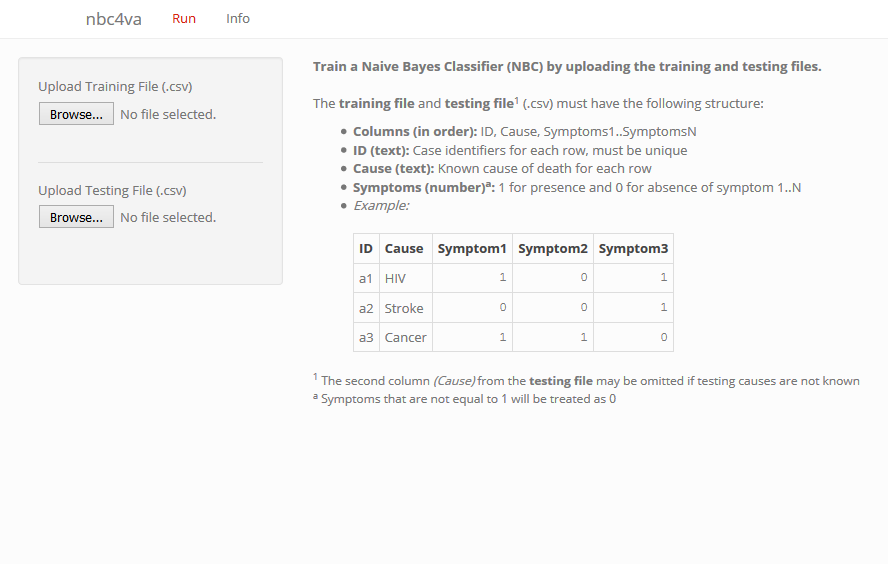
Usage
nbc4vaGUI()
Details
This function requires the shiny package, which can be installed via:
install.packages("shiny")
Use esc in the R console to stop the GUI.
Please use a modern browser (e.g. latest firefox, chrome) for the best experience.
Value
Creates a GUI for running nbc4va in a web browser.
See Also
Other utility functions:
nbc4vaIO()
Examples
## Not run:
library(nbc4va)
nbc4vaGUI()
## End(Not run)
Run nbc4va using file input and output
Description
Runs nbc and uses summary.nbc on input data files or dataframes to output
result files or dataframes with data on predictions, probabilities, causes, and performance metrics in an easily accessible way.
Usage
nbc4vaIO(
trainFile,
testFile,
known = TRUE,
csmfaFile = NULL,
saveFiles = TRUE,
outDir = dirname(testFile),
fileHeader = strsplit(basename(testFile), "\\.")[[1]][[1]],
fileReader = read.csv,
fileReaderIn = "file",
fileReaderArgs = list(as.is = TRUE),
fileWriter = write.csv,
fileWriterIn = "x",
fileWriterOut = "file",
fileWriterArgs = list(row.names = FALSE),
outExt = "csv"
)
Arguments
trainFile |
A character value of the path to the data to be used as the train argument for |
testFile |
A character value of the path to the data to be used as the test argument for |
known |
TRUE to indicate that the test causes are available in the 2nd column and FALSE to indicate that they are not known |
csmfaFile |
A character value of the path to the data to be used as the csmfa.obs argument for
|
saveFiles |
Set to TRUE to save the return object as files or FALSE to return the actual object |
outDir |
A character value of the path to the directory to store the output results files. |
fileHeader |
A character value of the file header name to use for the output results files.
|
fileReader |
A function that is able to read the trainFile and the testFile.
|
fileReaderIn |
A character value of the fileReader argument name that accepts a file path for reading as an input. |
fileReaderArgs |
A list of the fileReader arguments to be called with |
fileWriter |
A function that is able to write
|
fileWriterIn |
A character value of the fileWriter argument name that accepts a dataframe for writing. |
fileWriterOut |
A character value of the fileWriter argument name that accepts a file path for writing as an output. |
fileWriterArgs |
A list of arguments of the fileWriter arguments to be called with |
outExt |
A character value of the extension (without the period) to use for the result files.
|
Details
See Methods documentation for details on the methodology and implementation of the Naive Bayes Classifier algorithm. This function may also act as a wrapper for the main nbc4va package functions.
Value
out Vector or list of respective paths or data from the naive bayes classifier:
If (saveFiles is TRUE) return a named character vector of the following:
Names: dir, pred, prob, causes, summary
dir (char): the path to the directory of the output files
pred (char): the path to the prediction table file, where the columns of Pred1..PredN are ordered by the prediction probability with Pred1 being the most probable cause
prob (char): the path to the probability table file, where the columns excluding the CaseID are the cause and each cell has a probability value
causes (char): the path to the cause performance metrics table file, where each column is a metric and each row is a cause
metrics (char): the path to the overall performance metrics table file, where each column is a metric
If (saveFiles is FALSE) return a list of the following:
Names: pred, prob, causes, summary
pred (dataframe): the prediction table, where the columns of Pred1..PredN are ordered by the prediction probability with Pred1 being the most probable cause
prob (dataframe): the probability table, where the columns excluding the CaseID are the cause and each cell has a probability value
causes (dataframe): the cause performance metrics table, where each column is a metric and each row is a cause
metrics (dataframe): the summary table, where each column is a performance metric
nbc (object): the returned
nbcobjectnbc_summary (object): the returned
summary.nbcobject
See Also
Other utility functions:
nbc4vaGUI()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaData)
# Split data into train and test sets
train <- nbc4vaData[1:50, ]
test <- nbc4vaData[51:100, ]
# Save train and test data as csv in temp location
trainFile <- tempfile(fileext=".csv")
testFile <- tempfile(fileext=".csv")
write.csv(train, trainFile, row.names=FALSE)
write.csv(test, testFile, row.names=FALSE)
# Use nbc4vaIO via file input and output
# Set "known" to indicate whether test causes are known
outFiles <- nbc4vaIO(trainFile, testFile, known=TRUE)
# Use nbc4vaIO as a wrapper
out <- nbc4vaIO(train, test, known=TRUE, saveFiles=FALSE)
Translate open verbal autopsy arguments to train a NBC model
Description
A wrapper function for creating an nbc object with the parameters specified by the openVA package.
Usage
ova2nbc(symps.train, symps.test, causes.train, causes.table = NULL, ...)
Arguments
symps.train |
Dataframe of verbal autopsy train data.
Example:
| ||||||||||||||||||||
symps.test |
Dataframe of verbal autopsy test data in the same format as symps.train.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
causes.train |
The train vector or column for the causes of death to use.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
causes.table |
Character list of unique causes to learn.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
... |
Additional arguments to be passed to avoid errors if necessary. |
Value
nbc An nbc object with the following modifications:
$id (vectorof char): set to test data ids
$prob (matrixof numeric): set to a matrix of likelihood for each cause of death for the test cases
$CSMF (vectorof char): set to the predicted CSMFs with names for the corresponding causes
References
Li Z, McCormick T, Clark S. openVA: Automated Method for Verbal Autopsy [Internet]. 2016. [cited 2016 Apr 29]. Available from: https://cran.r-project.org/package=openVA
Examples
## Not run:
library(openVA) # install.packages("openVA")
library(nbc4va)
# Obtain some openVA formatted data
data(RandomVA3) # cols: deathId, cause, symptoms..
train <- RandomVA3[1:100, ]
test <- RandomVA3[101:200, ]
# Run naive bayes classifier on openVA data
results <- ova2nbc(train, test, "cause")
# Obtain the probabilities and predictions
prob <- results$prob.causes
pred <- results$pred.causes
## End(Not run)
Bar plot of top predicted causes from a NBC model
Description
Plots the results from a nbc object as a barplot for a number of causes based on
predicted Cause Specific Mortality Fraction (CSMF).
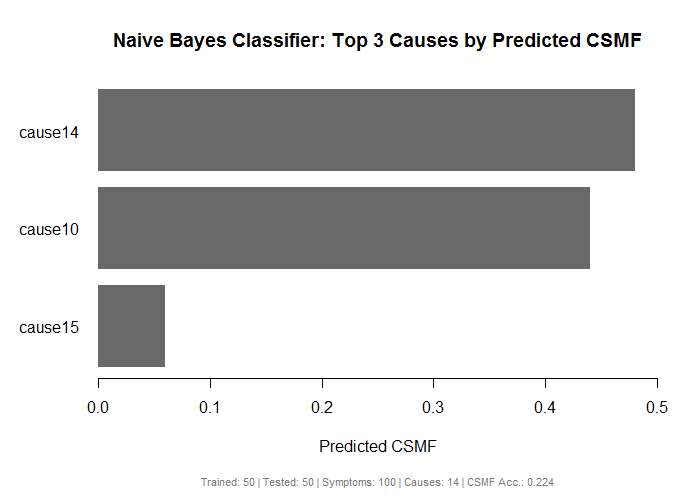
Usage
## S3 method for class 'nbc'
plot(
x,
top.plot = length(x$causes.pred),
min.csmf = 0,
csmfa.obs = NULL,
footnote = TRUE,
footnote.color = "gray48",
footnote.size = 0.7,
main = paste("Naive Bayes Classifier: Top ", top.plot, " Causes by Predicted CSMF",
sep = ""),
xlab = "Predicted CSMF",
col = "dimgray",
horiz = TRUE,
border = NA,
las = 1,
...
)
Arguments
x |
A |
top.plot |
A number that produces top k causes depending on a Cause Specific Mortality Fraction (CSMF) measure. |
min.csmf |
A number that represents the minimum CSMF measure for a cause to be included in the plot. |
csmfa.obs |
A character vector of the true causes for calculating the CSMF accuracy. |
footnote |
A boolean indicating whether to include a footnote containing details about the nbc or not. |
footnote.color |
A character specifying the color of the footnote text. |
footnote.size |
A numeric value specifying the size of the footnote text. |
main |
A character value of the title to display. |
xlab |
A character value of the x axis title. |
col |
A character value of the color to use for the plot. |
horiz |
Set to TRUE to draw bars horizontally and FALSE to draw bars vertically. |
border |
A character value of the colors to use for the bar borders. Set to NA to disable. |
las |
An integer value to determine if labels should be parallel or perpendicular to axis. |
... |
Additional arguments to be passed to |
Details
See Methods documentation for details on CSMF and CSMF accuracy.
Value
Generates a bar plot the top predicted causes from the NBC model
See Also
Other main functions:
nbc(),
print.nbc_summary(),
summary.nbc()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaData)
# Run naive bayes classifier on random train and test data
train <- nbc4vaData[1:50, ]
test <- nbc4vaData[51:100, ]
results <- nbc(train, test)
# Plot the top 3 causes by CSMF
plot(results, top.plot=3)
Print top predicted causes from a NBC model
Description
Prints a summary message from a summary.nbc object of
the top causes by probability or predicted Cause Specific Mortality Fraction (CSMF).
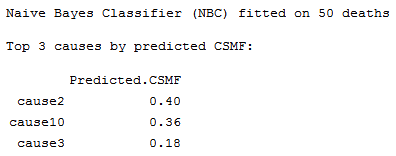
Usage
## S3 method for class 'nbc_summary'
print(x, ...)
Arguments
x |
A |
... |
Additional arguments to be passed if applicable. |
Details
See Methods documentation for details on CSMF and probability from the Naive Bayes Classifier.
Value
Prints a summary of the top causes of death by probability for the NBC model.
See Also
Other main functions:
nbc(),
plot.nbc(),
summary.nbc()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaData)
# Run naive bayes classifier on random train and test data
train <- nbc4vaData[1:50, ]
test <- nbc4vaData[51:100, ]
results <- nbc(train, test)
# Print a summary of all the test data for the top 3 causes by predicted CSMF
brief <- summary(results, top=3)
print(brief)
Summarize a NBC model with metrics
Description
Summarizes the results from a nbc object. The summary
can be either for a particular case or for the entirety of cases.
Usage
## S3 method for class 'nbc'
summary(object, top = 5, id = NULL, csmfa.obs = NULL, ...)
Arguments
object |
The result |
top |
A number that produces top causes depending on id:
|
id |
A character representing a case id in the test data. |
csmfa.obs |
A character vector of the true causes for calculating the CSMF accuracy. |
... |
Additional arguments to be passed if applicable |
Details
See Methods documentation for details on calculations and metrics.
Value
out A summary object built from a nbc object with modifications/additions:
If (id is char):
Additions to a
nbcobject:$id (char): the case id chosen by the user
$top (numeric): the input number of top causes for id
$top.prob (vectorof double): the top probabilities for id
The following are modified from a nbc object to be id specific:
$test, $test.ids, $test.causes, $obs.causes, $prob, $prob.causes, $pred, $pred.causes
If (id is NULL):
Additions to the
nbcobject:* indicates that the item is only available if test causes are known
** indicates that the item ignores * if csmfa.obs is given
$top.csmf.pred (vectorof double): the top predicted CSMFs by cause
$top.csmf.obs* (vectorof double): the top observed CSMFs by cause
$metrics.all** (vectorof double): a numeric vector of overall metrics.
Names: TruePositives, TrueNegatives, FalsePositives, FalseNegatives, Accuracy, Sensitivity, PCCC, CSMFMaxError, CSMFaccuracy
TruePositives* (double): total number of true positives
TrueNegatives* (double): total number of true negatives
FalsePositives* (double): total number of false positives
FalseNegatives* (double): total number of false negatives
Sensitivity* (double): the overall sensitivity
PCCC* (double): the partial chance corrected concordance
CSMFMaxError** (double): the maximum Cause Specific Mortality Fraction Error
CSMFaccuracy** (double): the Cause Specific Mortaliy Fraction accuracy
$metrics.causes (dataframe): a perfomance table of metrics by cause.
Columns: Cause, Sensitivity, CSMFpredicted, CSMFobserved
Cause (vectorof char): The unique causes from both the obs and pred inputs
Sensitivity* (vectorof double): the sensitivity for a cause
CSMFpredicted (vectorof double): the cause specific mortality fraction for a cause given the predicted deaths
CSMFobserved* (vectorof double): the cause specific mortality fraction for a cause given the observed deaths
TruePositives (vectorof double): The total number of true positives per cause
TrueNegatives (vectorof double): The total number of true negatives per cause
FalsePositives (vectorof double): The total number of false positives per cause
FalseNegatives (vectorof double): The total number of false negatives per cause
PredictedFrequency (vectorof double): The occurence of a cause in the pred input
ObservedFrequency (vectorof double): The occurence of a cause in the obs input
Example:
Cause Sensitivity Metric-n.. HIV 0.5 #.. Stroke 0.5 #..
See Also
Other main functions:
nbc(),
plot.nbc(),
print.nbc_summary()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaData)
# Run naive bayes classifier on random train and test data
train <- nbc4vaData[1:50, ]
test <- nbc4vaData[51:100, ]
results <- nbc(train, test)
# Obtain a summary for the results
brief <- summary(results, top=2) # top 2 causes by CSMF for all test data
briefID <- summary(results, id="v48") # top 5 causes by probability for case "v48"
Cause of death predictions from a NBC model
Description
Obtains the top causes of deaths for each testing case from a result nbc object.
Usage
topCOD.nbc(object)
Arguments
object |
The result |
Value
out A dataframe of the top CODs:
Columns: ID, COD
ID (vectorof char): The ids for each testing case
COD (vectorof char): The top prediction for each testing case
See Also
Other wrapper functions:
csmf.nbc()
Examples
library(nbc4va)
data(nbc4vaData)
# Run naive bayes classifier on random train and test data
train <- nbc4vaData[1:50, ]
test <- nbc4vaData[51:100, ]
results <- nbc(train, test)
# Obtain the top cause of death predictions for the test data
topPreds <- topCOD.nbc(results)