

kuzuR provides an R interface to the Kuzu Graph Database, a
high-performance, embedded graph database. The package acts as a wrapper
around the official Python kuzu client, using the
reticulate package to bridge the two languages. This allows
you to interact with Kuzu seamlessly within your R environment,
integrating its powerful graph computation capabilities into your
existing data analysis workflows.
The primary goal of kuzuR is to provide an idiomatic R
experience for: - Creating and managing Kuzu database instances. -
Executing Cypher queries. - Loading data from and retrieving results
into R data frames and tibbles. - Converting graph query results
directly into R-native graph objects like igraph and
tidygraph.
kuzuR requires a working Python installation with the
kuzu, pandas, and networkx
packages.
You can install the development version from GitHub:
# install.packages("pak")
pak::pak("WickM/kuzuR")Or the stable version from CRAN:
# install.packages("kuzuR")After installing kuzuR, you must install the required
Python packages. You can do this from your R console using
reticulate:
library(kuzuR)
reticulate::py_install(c("kuzu", "pandas", "networkx"), pip = TRUE)You can check that all dependencies are correctly installed by running:
check_kuzu_installation()
#> The 'kuzu', 'pandas', and 'networkx' Python packages are installed and available.Here is a complete example demonstrating how to create a database, define a schema, load data, and run queries.
library(kuzuR)
library(igraph)
library(tidygraph)
# 1. Create a database in a temporary directory
db_path <- tempfile()
con <- kuzu_connection(db_path)
# 2. Define a schema
# Create a 'Person' node table with a STRING name and INT64 age
schema_query_1 <- "CREATE NODE TABLE Person (
name STRING,
age INT64,
PRIMARY KEY (name)
)"
kuzu_execute(con, schema_query_1)
#> <kuzu.query_result.QueryResult object at 0x000001DDFFE00050>
# Create a 'Knows' relationship table
schema_query_2 <- "CREATE REL TABLE Knows(FROM Person TO Person, since INT64)"
kuzu_execute(con, schema_query_2)
#> <kuzu.query_result.QueryResult object at 0x000001DDFFC97D90>
# 3. Load data from R data frames
# Create node data
nodes <- data.frame(
name = c("Alice", "Bob", "Carol"),
age = c(30, 40, 50)
)
# Create edge data
edges <- data.frame(
from_person = c("Alice", "Bob"),
to_person = c("Bob", "Carol"),
since = c(2010, 2015)
)
# Use kuzu_copy_from_df to load the data
kuzu_copy_from_df(con, nodes, "Person")
names(edges) <- c("FROM", "TO", "since")
kuzu_copy_from_df(con, edges, "Knows")
# 4. Execute Cypher queries
# Retrieve data as a data frame
query_result <- kuzu_execute(con, "MATCH (p:Person) RETURN p.name, p.age")
as.data.frame(query_result)
#> p.name p.age
#> 1 Alice 30
#> 2 Bob 40
#> 3 Carol 50
# 5. Convert graph results to R objects
# The same query result can be converted into different graph formats.
graph_result <- kuzu_execute(con, "MATCH (a:Person)-[k:Knows]->(b:Person) RETURN a, k, b")
# a) Convert to an igraph object
g_igraph <- as_igraph(graph_result)
print(g_igraph)
#> IGRAPH 6697a05 DN-- 3 2 --
#> + attr: name (v/c), age (v/n), Person (v/l), label (v/c), _label (e/c),
#> | _id (e/x), _dst (e/x), since (e/n), _src (e/x)
#> + edges from 6697a05 (vertex names):
#> [1] Person_Alice->Person_Bob Person_Bob ->Person_Carol
plot(g_igraph)
# b) Convert to a tidygraph object
g_tidy <- as_tidygraph(graph_result)
print(g_tidy)
#> # A tbl_graph: 3 nodes and 2 edges
#> #
#> # A rooted tree
#> #
#> # Node Data: 3 × 4 (active)
#> name age Person label
#> <chr> <dbl> <lgl> <chr>
#> 1 Person_Alice 30 TRUE Person
#> 2 Person_Bob 40 TRUE Person
#> 3 Person_Carol 50 TRUE Person
#> #
#> # Edge Data: 2 × 7
#> from to `_label` `_id` `_dst` since `_src`
#> <int> <int> <chr> <list> <list> <dbl> <list>
#> 1 1 2 Knows <named list [2]> <named list [2]> 2010 <named list [2]>
#> 2 2 3 Knows <named list [2]> <named list [2]> 2015 <named list [2]>
# 6. Inspecting Query Results
# You can inspect the schema of a query result without converting it to a data frame.
# Get column names
kuzu_get_column_names(query_result)
#> [1] "p.name" "p.age"
# Get column data types
kuzu_get_column_data_types(query_result)
#> [1] "STRING" "INT64"
# Get the full schema as a named list
kuzu_get_schema(query_result)
#> $p.name
#> [1] "STRING"
#>
#> $p.age
#> [1] "INT64"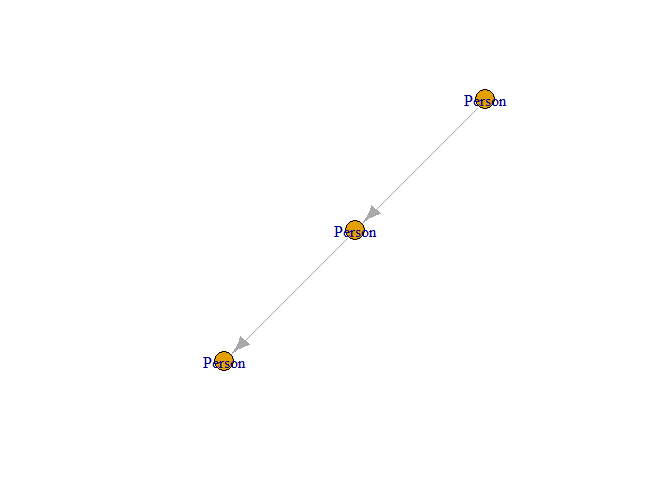
Plot of the graph structure created from Kuzu query results.